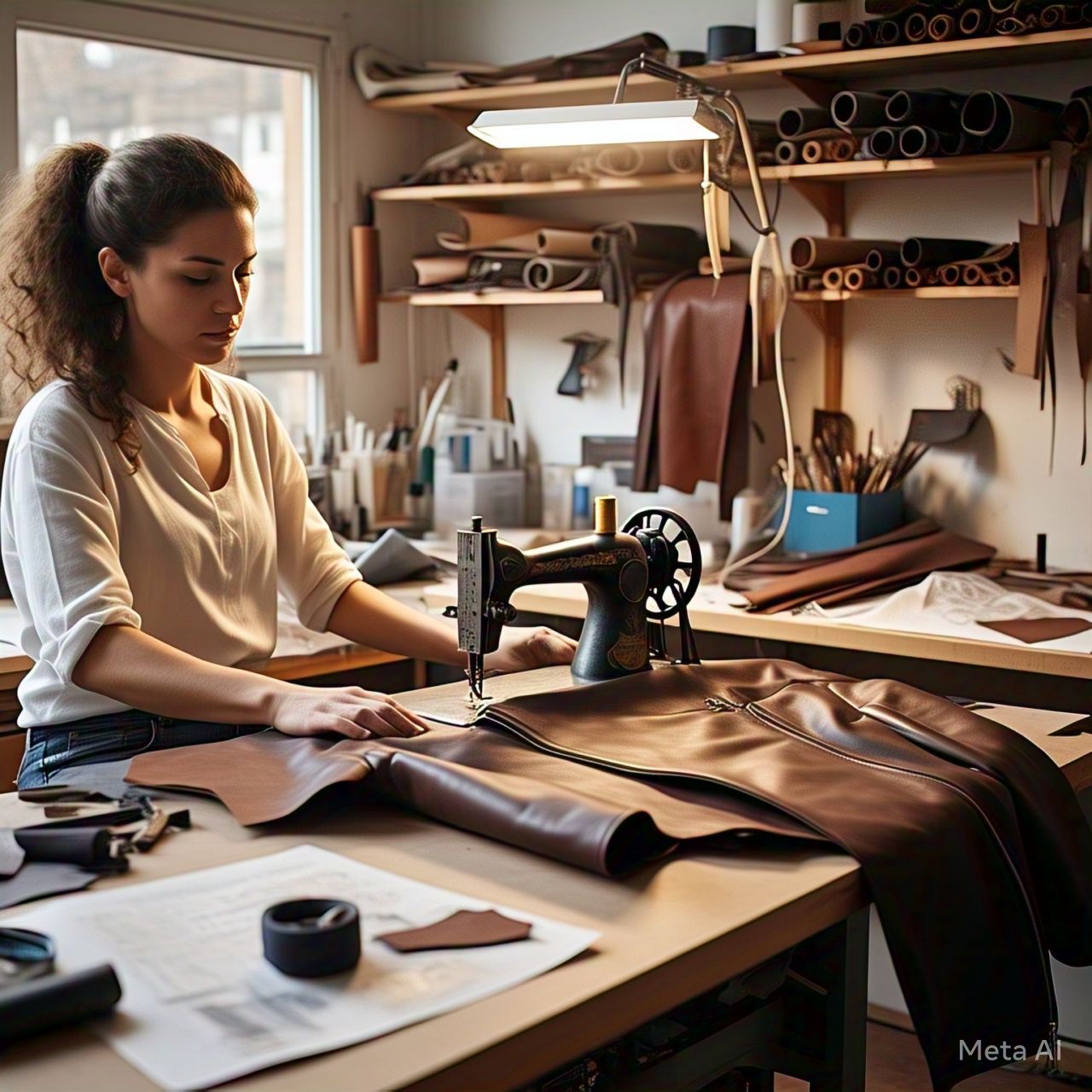

How Leather Jackets Are Made: The Craft Behind Timeless Style
Leather jackets have been a symbol of style, rebellion, and craftsmanship for decades. But have you ever wondered how these iconic pieces are created? From selecting premium leather to the finishing touches, making a leather jacket is a meticulous process that combines artistry and skill. At FEASSA, we value this timeless craftsmanship and want to share with you the secrets behind creating a leather jacket.
In this guide, we'll walk you through how leather jackets are made, what tools and techniques are involved, and how you can get started on your own leatherworking journey.
Step 1: Selecting the Leather
The journey to creating a leather jacket starts with the selection of leather. Not all leather is created equal, and the quality of the leather will determine the jacket’s durability, softness, and appearance. Cowhide, lambskin, and goatskin are commonly used for jackets, with each offering its own characteristics. Cowhide is known for its toughness, while lambskin is softer and more flexible.
At FEASSA, we use only premium leather to ensure the final product not only looks great but stands the test of time. High-quality leather also ages beautifully, developing a unique patina over the years.
Step 2: Cutting the Leather
Once the leather is selected, it is carefully measured and cut into the shapes that will make up the jacket’s panels. Leather is thick and tough, which makes the cutting process challenging, requiring precise measurements to ensure the pieces fit perfectly when assembled.
Pattern templates are used to ensure that every part of the jacket — from the sleeves and back panels to the collar and cuffs — are in the right proportions. This step is crucial for ensuring that the jacket’s fit and style are exactly what the designer envisioned.
Step 3: Stitching and Assembly
The next step involves stitching the leather pieces together. Leather stitching requires precision and care, as leather is much tougher than most fabrics. It’s stitched using either hand sewing or a machine, depending on the design and the level of craftsmanship required.
At FEASSA, we use double-needle stitching for durability, especially in areas that experience more stress like the shoulder seams or around the zippers. Every stitch must be neat and consistent to maintain the jacket’s structure and aesthetic appeal.
Step 4: Adding Finishing Touches
Once the jacket is assembled, the final touches are added. This includes installing zippers, buttons, and snap closures, and reinforcing features like the collar and cuffs. The jacket may also go through a process of dyeing to achieve the desired color, and conditioning to soften the leather and restore its natural sheen.
Some jackets are distressed to create a vintage look, adding to their personality and style. This step is about giving the jacket character and ensuring it fits the design style.
Step 5: Final Inspection and Quality Control
The last step is the final inspection. This ensures the leather jacket meets the highest standards for both style and durability. The stitching is checked, the fit is tested, and the leather is conditioned one last time to make sure it’s ready for wear. Once approved, the jacket is packaged and shipped, ready to be worn and admired.
Tips for Getting Started with Leather Jacket Making
Creating a leather jacket is a skill that requires practice and patience. If you're interested in making your own leather goods or even your first jacket, here are some tips to get you started:
✅ Start Small
If you're new to leatherworking, start with smaller projects like wallets or belts to get a feel for the material. This will help you understand how leather behaves when cut, stitched, and dyed.
✅ Invest in Quality Tools
For beginners, some essential tools include sharp rotary cutters, leather needles, waxed thread, cutting mats, and a punch tool for making holes. You don’t need to rush out and buy an industrial machine right away — a hand sewing kit will do for initial projects.
✅ Learn the Basics of Leather Types
Understanding the different types of leather and their uses is key. Lambskin is soft but delicate, while cowhide is durable and perfect for jackets. Experiment with different types to see how they perform in different conditions.
✅ Stitching is Key
Leather stitching is one of the most important skills to master. Start with simple straight stitches and work your way up to more complex techniques. Consistent and clean stitching is crucial to a jacket's durability.
✅ Dyeing and Conditioning
Dyeing leather can be a fun process, but always test your dye on a scrap piece of leather before applying it to the whole jacket. After dyeing, use leather conditioner to keep your creation soft and long-lasting.
Essential Equipment for Leatherworking
If you’re eager to start making leather jackets or other leather items, here’s a list of the essential equipment you’ll need:
-
Cutting Tools:
-
Leather scissors or rotary cutter
-
Leather hole puncher
-
Ruler for measuring
-
-
Stitching Tools:
-
Leather needles
-
Waxed thread
-
Stitching awl
-
Thimble
-
-
Dyeing and Conditioning Tools:
-
Leather dye (water-based for a smooth finish)
-
Leather conditioner
-
Paintbrushes for dyeing
-
-
Sewing Machine (Optional):
-
If you plan to make larger pieces, a heavy-duty sewing machine designed for leather can save time.
-
-
Burnishing Tools:
-
Used to smooth and finish the edges of your leather project for a professional look.
-
Conclusion
Making a leather jacket is a blend of art, craftsmanship, and passion. From selecting the perfect leather to stitching it together, the process requires patience, skill, and attention to detail. Whether you want to try leatherworking yourself or are looking for a timeless piece made by professionals, FEASSA has you covered with jackets that combine style and durability.
Explore our collection of leather jackets at FEASSA and find the perfect piece to suit your unique style and taste.








Dejar un comentario
Este sitio está protegido por hCaptcha y se aplican la Política de privacidad de hCaptcha y los Términos del servicio.